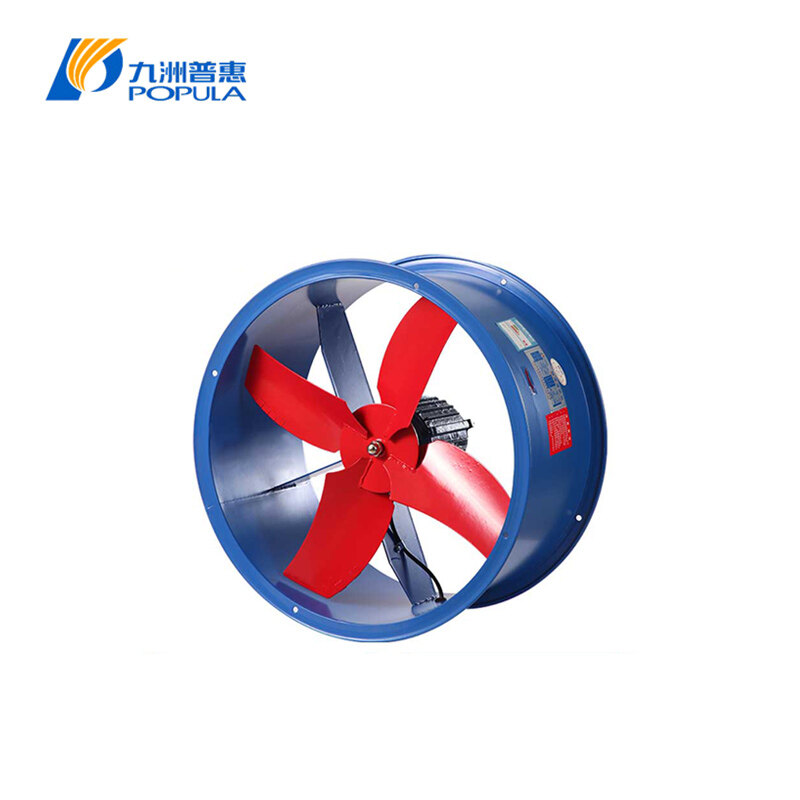
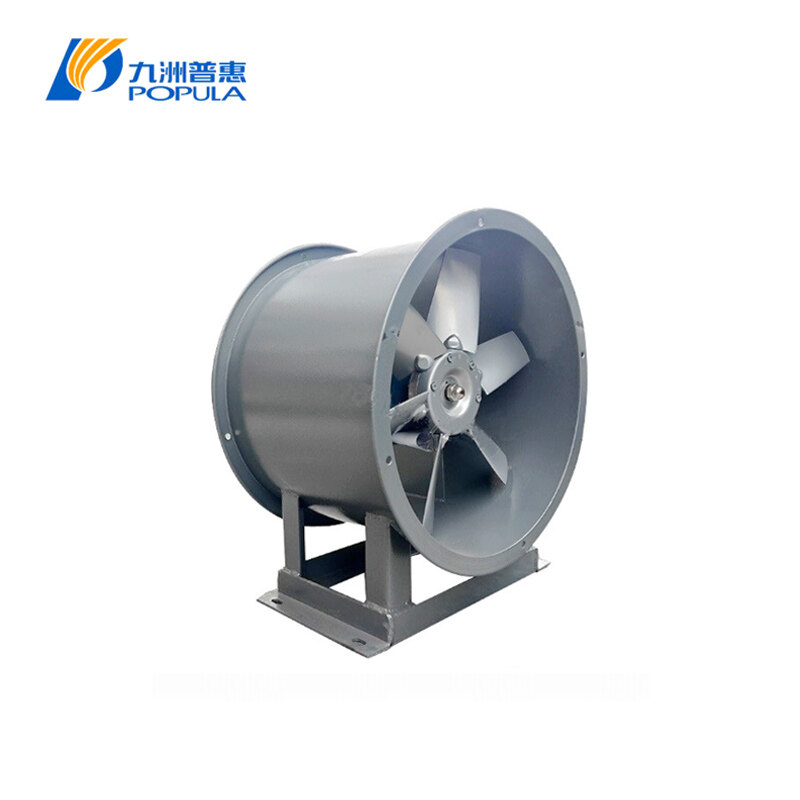
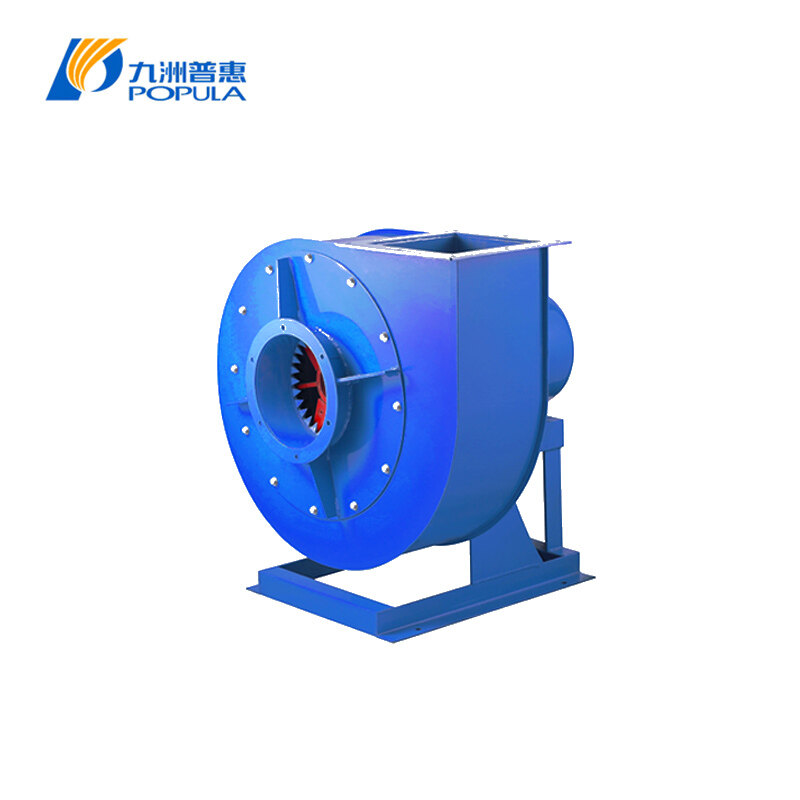
In industrial and commercial settings, ventilation is critical for maintaining air quality, controlling temperature, and ensuring equipment efficiency. Axial fans are commonly used due to their ability to move large volumes of air with relatively low energy consumption. However, when choosing the right axial fan for your system, understanding the axial fan air flow direction is crucial. Selecting the appropriate direction can optimize performance, energy efficiency, and operational safety.
But how do you know which air flow direction is suitable for your application? This article will explore the key factors that influence axial fan air flow direction and offer practical tips on making the right choice.
What Is Axial Fan Air Flow Direction?
The axial fan air flow direction refers to how air moves through the fan. There are two primary air flow directions:
Forward Curved Air Flow (Blowing): This occurs when the fan blows air in the direction of the fan's rotation.
Backward Curved Air Flow (Suction): In this case, the fan pulls air in from behind and pushes it forward, away from the fan.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Air Flow Direction
When selecting the right axial fan air flow direction, several factors should be considered. Each of these factors plays a role in the overall performance and suitability of the fan for your ventilation system.
1. Application Type
The nature of your application dictates whether you need air to be blown directly onto a surface or drawn away from it. For example:
Cooling applications: In industries where machinery generates heat, a forward curved air flow might be ideal to ensure hot air is directed away from the equipment, keeping it cool.
Exhaust systems: If you're looking to remove contaminants or control air quality, a backward curved air flow is preferable for pulling air from the room and expelling it outside.
2. Air Flow and Pressure Requirements
Some applications require high pressure to overcome resistance in ductwork or filters. Fans that operate with backward curved air flow typically provide better performance in high-pressure systems, as they can manage resistance more effectively. Meanwhile, forward curved fans are more suited to systems that prioritize air volume over pressure.
3. Installation Space
The size and configuration of your installation space can also determine which air flow direction is more appropriate. In confined spaces where clearance is limited, the backward curved option may provide more flexibility by drawing air from restricted areas. On the other hand, forward curved fans may be preferred in systems with ample space to ensure proper air distribution.
4. Noise Level
Noise control is often a critical factor in ventilation systems, particularly in sensitive environments like hospitals or offices. Backward curved fans are typically quieter than their forward curved counterparts, making them a good choice for applications where minimal noise is essential.
How to Optimize Axial Fan Performance
1. Select the Correct Fan Size
Choosing the right fan size is vital to ensure your system runs efficiently. Oversized fans can waste energy, while undersized ones may struggle to meet air flow demands. Make sure to consult fan specifications to match the fan to your system's requirements.
2. Regular Maintenance
Proper maintenance of your axial fan is essential to maintaining its efficiency. Cleaning the fan blades and checking for obstructions in the ductwork will ensure consistent performance, regardless of the air flow direction.
3. Optimize Blade Design
The blade design of your axial fan can significantly impact performance. Blades with optimal curvature will help direct air flow more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and noise levels.
Common Applications of Axial Fans
Axial fans are widely used across various industries due to their versatility and energy efficiency. Below are some common applications where axial fan air flow direction plays a critical role:
1. HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, axial fans are often used to regulate indoor air quality and temperature. The fan's air flow direction is critical in determining whether it is supplying fresh air or exhausting stale air.
2. Industrial Exhaust Systems
Axial fans are commonly used in factories and warehouses to remove hazardous fumes and contaminants. In such settings, backward curved air flow fans are generally preferred to efficiently extract polluted air.
3. Cooling for Electronic Equipment
In server rooms or electronic manufacturing plants, maintaining a stable temperature is essential. Axial fans with forward curved air flow can help dissipate heat, preventing equipment failure.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
When it comes to selecting the right axial fan air flow direction, it's important to consider the specific needs of your application. Factors like the type of system, pressure requirements, and noise levels all influence which direction is more appropriate. By understanding these aspects, you can choose an axial fan that not only meets your operational demands but also enhances energy efficiency and system longevity.
At AMX, we offer a range of custom ventilation system solutions designed to meet the needs of various industrial applications. Whether you're looking for high-performance axial fans optimized for cooling, exhaust, or general air movement, we have the expertise to help you choose the right product for your system. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist with your ventilation needs.